Check out the latest news from Biotium USA, a leading provider of innovative fluorescent solutions for scientists.
Biotium is devoted to providing high-quality and innovative fluorescent tools that fuel scientific discovery.
Since its founding in 2001, Biotium has developed over 30 patented technologies including GelRed® dyes, CF® Dyes, NucView® Caspase-3 Substrates, EvaGreen® Dyes, and TrueBlack® Background Reducers.
-
BIOTIUM | Protocol: Maleimide Labelling of Protein Thiol
Maleimide labelling of antibodies can be used as an alternative to succinimidyl ester labelling of amines, for antibodies where amine labelling affects the antibody binding affinity.
Read More -
BIOTIUM | Protocol: Aminooxy Labelling of Glycoproteins
Aminooxy labelling can be used to conjugate glycoproteins after oxidation of the carbohydrates to generate aldhehyde groups.
Read More -
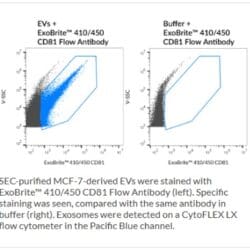
BIOTIUM | ExoBrite™ Flow Antibody Conjugates
Validated Antibodies for Detection of EV Markers by Flow Cytometry The most common proteins used as EV markers are CD9, CD63, and CD81, members of the tetraspanin family. While antibodies targeting these proteins are available by commercial suppliers, few are validated or perform well for detection of EVs or exosomes. The antibodies and dye labels […]
Read More -
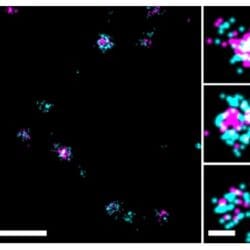
BIOTIUM | SUPER-RESOLUTION IMAGING
High-Performance EV Stains for Super-Resolution Featuring STORM-Optimized CF® Dyes Characterizing exosomes and EVs by imaging is challenging due to their small size and the resolution limits of conventional light microscopy. Super-resolution techniques like direct stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (dSTORM) overcome these limits, providing single-molecule resolution of subcellular structures such as EVs. This enables deeper insights […]
Read More -
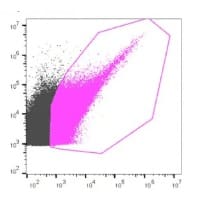
BIOTIUM | ExoBrite™ Antibody Cocktails
Streamline Your Workflows with High-Coverage EV Staining or Robust Phenotype Analysis
Read More -
BIOTIUM | Biotium’s ExoBrite™ Flow Antibody helps validate an upscaling protocol for potential exosome-based therapies
Exosome-based therapies are gaining attention in regenerative medicine for their ability to modulate cellular behaviour and enhance tissue repair. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have been shown to carry bioactive molecules such as proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids that facilitate intercellular communication and tissue regeneration. While MSC-derived exosomes have demonstrated therapeutic potential for […]
Read More -
BIOTIUM | Protocol: Cell Surface Antibody Staining for Flow Cytometry
There are many protocols for staining cells for flow cytometry. Protocols may to need be optimized for different cell types, targets, or applications. This is our basic protocol for extracellular staining of cell surface epitopes in suspension cells for flow cytometry.
Read More -
BIOTIUM | Protocol: Immunofluorescence Staining of Cells for Microscopy
There are many variations on IF protocols, and steps may need to be optimized for different targets or applications. Some epitopes may require specific fixation conditions for detection. This is our basic protocol for staining adherent cells in dishes or cells grown on coverslips.
Read More -
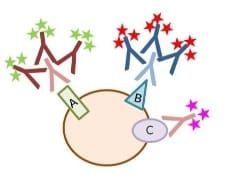
BIOTIUM | Tech Tip: Combined Direct and Indirect IF Using Primary Antibodies from the Same Host
Phalloidin Conjugates ORDER HERE Mix-n-Stain™ CF® Dye Antibody Labelling Kits ORDER HERE
Read More -
BIOTIUM | Tech Tip: Battling Tissue Autofluorescence
TrueBlack® Lipofuscin Autofluorescence Quencher, 20X in DMF ORDER HERE TrueBlack® Plus Lipofuscin Autofluorescence Quencher, 40X in DMSO ORDER HERE
Read More